本文
What is the reservoir? (English version)
1 The Three Major Cereals in the World
The three cereals, wheat, corn, and rice, most common staples of human beings, are called the three major cereals in the world.
Rice is cultivated mainly in Asia. Meanwhile wheat and corn are widely grown in European and American countries, not to mention in the other areas of the world but the Near and Middle East Asia.
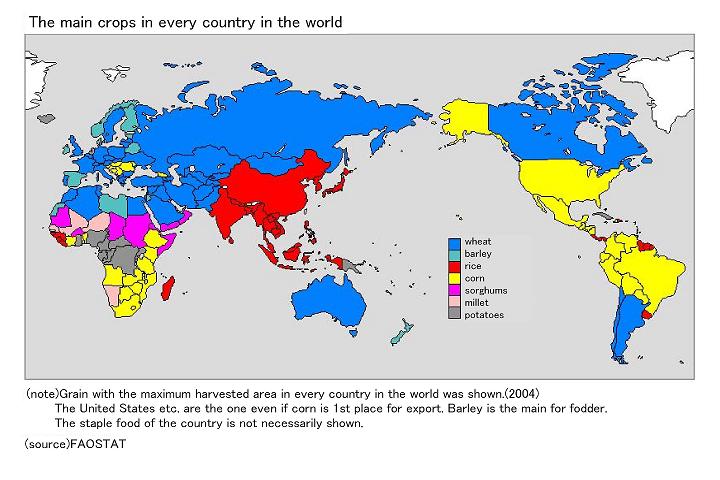
According to FAO, rice is the staple food for more than half of the world population. This means that more than half of the world people depends on rice, which cultivation is concentrated in Asia.
2 Rice Farming in Asian Monsoon Climate
Why is rice mainly grown in Asia?
One of the reasons is Asian climate.
Generally, the air above the continent is easier to become colder and hotter than the air above the ocean. In summer, the warmer air above the continent causes an updraft, resulting in winds with plenty moisture sweeping into the continent from the ocean. On the contrary, in winter, the warmer air above the ocean causes updraft, letting dry air above the continent flows out to the ocean.
This climate with seasonal winds is called a monsoon climate. In the region with this climate, the rainy season comes in summer, and the dry season in winter. As monsoon climates occupy large areas in Asia, it is distinguishably called Asian monsoon climate.
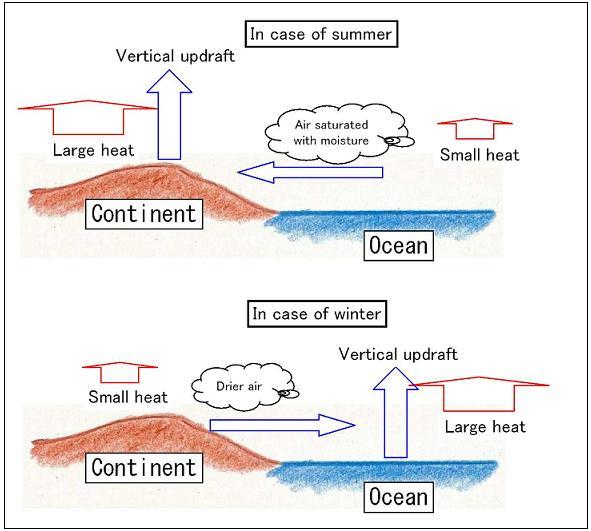
Movement of the atmosphere of every season
Annual rainfall distributions in three areas in Asia are as follows.
In Mumbai, India and Bangkok, Thailand, the rainy season and the dry season are clearly divided . In Wuhan, China, it does not have clear differences between the seasons, but still has high and low rainfall seasons.
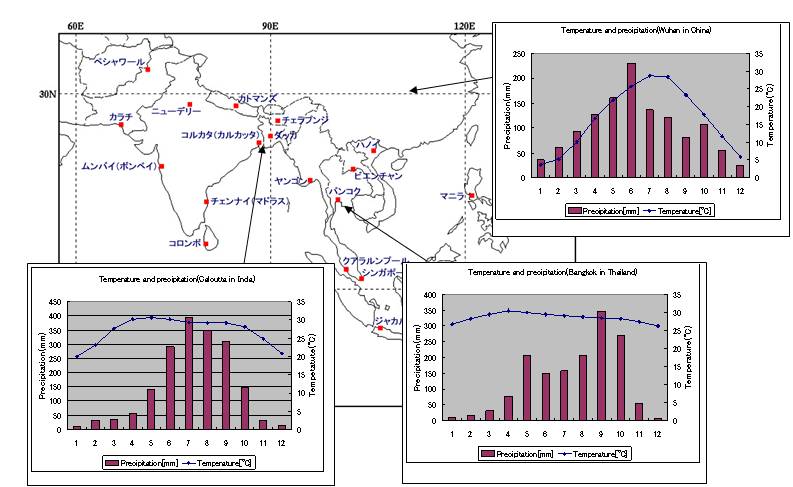
source:The Meteorological Agency"The weather data of the world"
3 Water Management and Events
In the region in Asian monsoon climate, the total rainfall is much more compared to regions in other climate, but the monthly precipitation is not stable . On the other hand, the rice cultivation needs appropriate amount of water in accordance with its growing stages. In ancient times when human beings started rice farming, it was neither stable nor efficient, because the water supply totally depended on real condition of rain. We used to can call it as rainfed farming
In order to alleviate this difficulty effectively, irrigation equipments and technologies have been developed to take water from rivers and supply it to fields, but due to the limited water resources water intake had not necessarily enough in many areas. . Farmers used to struggle with others to take much more water, especially in the old days. Then they settled rules of water allocation depended on the planting schedule. In addition, they shared materials and working days for maintenance and management of communal or public facilities such as ponds and canals. In China, Japan, Korea, India Sri Lanka, etc, many reservoirs were constructed to secure stable sources of water in the areas where river water was difficult to use. The reservoirs have been developed along with cooperative operations among them.
Those communities have been developed commonly the reservoirs and paddy fields. They used to hold events on the special occasions of rice farming, before or in planting and after harvesting, to express respects and appreciations to the gods and the nature. Such events are usually held near reservoirs, too.

Divine service that wishes good harvest.(Japan)
4 Rice Farming Supported by Reservoirs in Japan
It is said that paddy farming was brought to Japan from China 2700-3000 years ago, the last years of the ‘Jomon’ period. In the ‘Yayoi’ period, 2400-2700 years ago, life of people is a synonym with life of rice farming. In that era , intake weirs and canals were constructed for rice farming, and communities for the farming called “Mura” were formed, obsolete the ‘Jomon’ style with hunting lives. Since its introduction, the rice has supported the eating habits of Japanese people as a staple food.
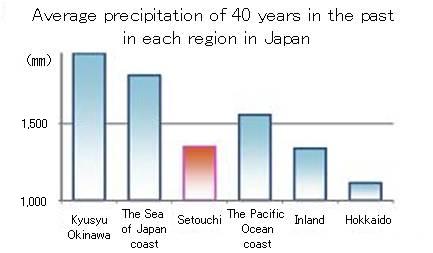
Japan surpasses the world average in annual precipitation per capita.
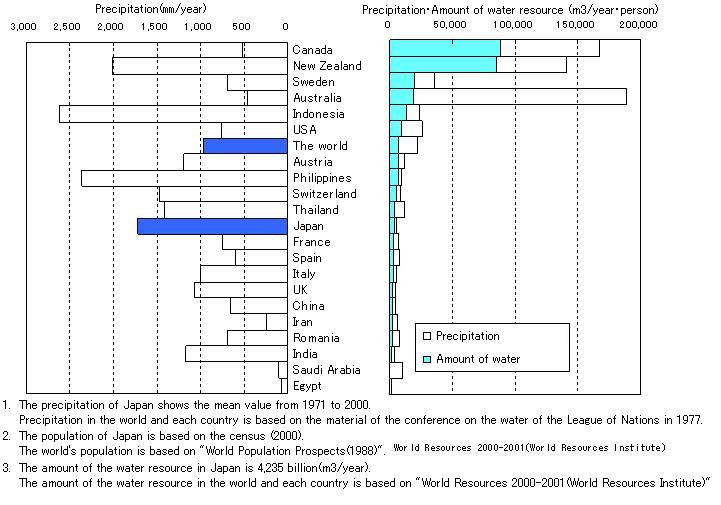
source:The Ministry of Land,Infrastructure and Transport
However, since rivers in Japan have sharp gradients, and the lengths are extremely short compared with prominent rivers in the world, the rainwater flows into the sea immediately after the rainfall. From this point, river water is not a stable source of water for rice farming.
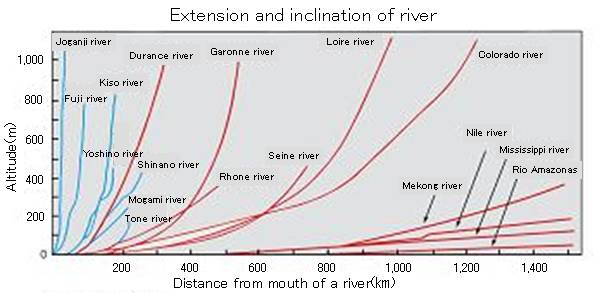
source:Yuu Takahashi"River engineering"(1990)
source:The Meteorological Agency
Therefore, reservoirs were widely developed over Japan to get stable irrigation water.
Today, approximately 210,000 reservoirs exist in Japan, and half of them are located in Hyogo and other prefectures in Setouchi region. Where stable water resources also are not available, such as an area of plateaus landscape, many reservoirs were constructed, too. Most of these reservoirs are still used as precious sources of water for rice farming now.
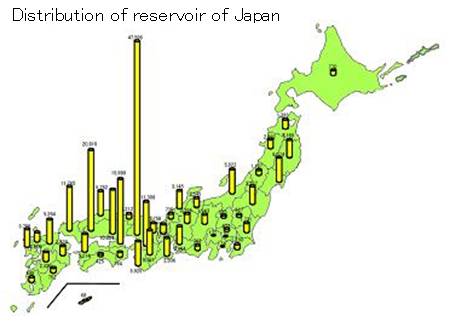
source:The Ministry of Agriculture,Forestry and Fisheries
Aichi prefecture has approximately 3,000 reservoirs for agriculture, which are the 15th largest number in Japan. The locations of those reservoirs are mainly divided into three large areas.
The first one is called Toyogawa area from Shinshiro City to Atsumi Peninsula through Toyohashi City. The second is called Yahagigawa area from Toyoda City to Hazu County. The third is called Owari-Chita area from Inuyama City to Chita Peninsula across the east part of Nagoya Metropolitan City.
These three areas did nott have enough water from rivers, because they were far from big rivers, and only flows of small rivers were insufficient for the sources of irrigation water.
Today, large canals had been constructed to supply water to the areas with chronic water shortage. To be specific, Toyogawa Canal in Toyogawa area, Yahagigawa Canal in Yahagigawa area, and Aichi Canal in Owari-Chita area which was completed by the first Japanese major project supported by World Bank loan are those.
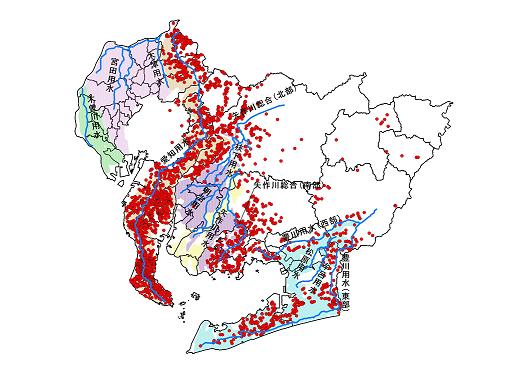
Reservoir distribution of Aichi Prefecture
Aichi Canal and Toyogawa Canal were completed as development projects with multipurpose including not only agricultural water, but municipal and industrial water.
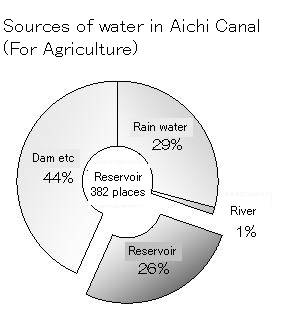
However, reservoirs in Aichi prefecture also still work as precious sources of water and support agriculture. In Aichi Canal area, a quarter of water for agriculture comes from reservoirs.
5 Roles of Reservoirs
○Water for Irrigation
In areas of insufficient water, the reservoirs are precious water resources for irrigation.
○Ecological Conservation
Flora and fauna thrive together around reservoirs. The balance of ecosystem is maintained by protecting not only reservoirs but also natural environment including forests , small streams and paddy around reservoirs.
○Relaxation Effects
People can feel relaxation when they see the nature around reservoirs. Some people also enjoy fishing on ponds.
○Alleviation of Disasters
When it rains heavily, reservoirs store the outflows of rainwater temporarily, and the water is used for fire-fighting in some areas.
Contact Information
Agricultural Land Planning Division, Agriculture and Forestry Infrastructure Office, Department of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Aichi Prefecture.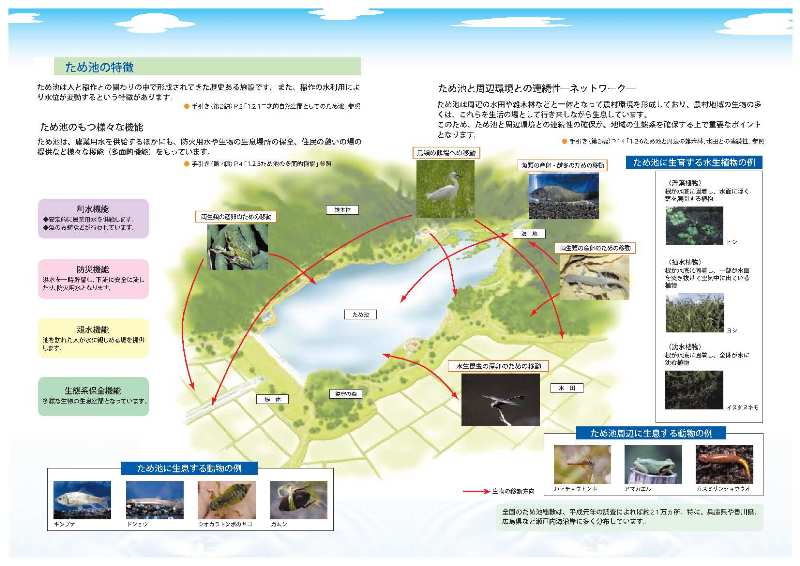
出典:農林水産省HPより

